When a well in an oilfield is first opened, generally there is plenty of existing pressure and volume for oil, gas and water to reach the surface. Over time, however, that initial boost reduces and artificial lift methods must be applied to literally push those resources to the surface. The most often used artificial lift methods include progressing cavity pumps (PCP), rod lift, plunger lift, gas lift, hydraulic lift, and electric submersible pumps (ESP). Each has particular strengths for specific applications.
Conventional pumping methods
Netzsch Pumps USA, in partnership with DXP, began a discussion with a Midwest oil producer that employed the gas lift method. The producer had just constructed a multi-pad well site having designed in the gas lift artificial lift method.
In this system, high pressure gas is injected into the well bore, which forces the fluids to the surface. Each well then feeds the gas and fluids to a dedicated two phase, horizontal separator, which divides a major portion of the gas from the well fluids. The gas is then directed back into the compressor to be re-injected into the well bore.
The liquids and residual gas (not separated in the initial phase) are sent to a vertical, two phase separator for additional processing. The residual gas rises to the top of the separator and is fed back to the compressor. The fluids consisting of oil, water and some solids are then forced into the pumping system to be transported through pipelines to a central processing facility (CPF) where the oil is now separated from the water. The CPF is approximately 15 miles from the well site.
Unreliability of conventional technology
To date, the most common method to move the fluids to the CPF has been the use of centrifugal pumps. However, in this case several issues are encountered when using centrifugal technology:
- Inability to handle the varying suction and discharge pressures and maintain consistent flow rates.
- Inability to handle the viscosity fluctuations and maintain consistent flow rates.
- Inability to handle solids that may be present in the fluids without extreme wear.
Centrifugal pumps are unable to maintain constant flows when suction pressures vary. This is also the case when discharge pressures fluctuate. In order to provide consistent flow rates, control valves and other instrumentation must be used to insure the centrifugal pump is operating at its best efficiency point (BEP). If not, the flows drop off substantially reducing production.
Viscosity fluctuations are challenging for centrifugal pumps because flow output is affected. For instance, as viscosity increases the flow rate of a centrifugal pump will begin to rapidly decrease, and production rates are reduced.
The high speed impeller rotation of centrifugal pumps cannot handle solids or abrasives without accelerated wear. Because of the high speeds (3,600 RPM) solids and abrasives can cause rapid wear of the impellers, resulting in reduced production and high maintenance costs.
Nemo PC pumps address issues
Netzsch Nemo PC pumps can manage fluctuations in suction and discharge pressures while maintaining a consistent flow rate. Variations in viscosity of the pumped fluid do not affect the flow rates, allowing production to continue at the highest levels required.
Pump speeds are controlled by VFDs to meet production flow rates. PC pumps can meet the pressure demands over the wide speed range.
Netzsch Nemo PC pumps can handle solids and abrasives that could be present in the fluid with very little wear. This is because there is low internal leakage (slip) inside the pumping elements which is the result of the properly sized compression fit between the rotor and stator.
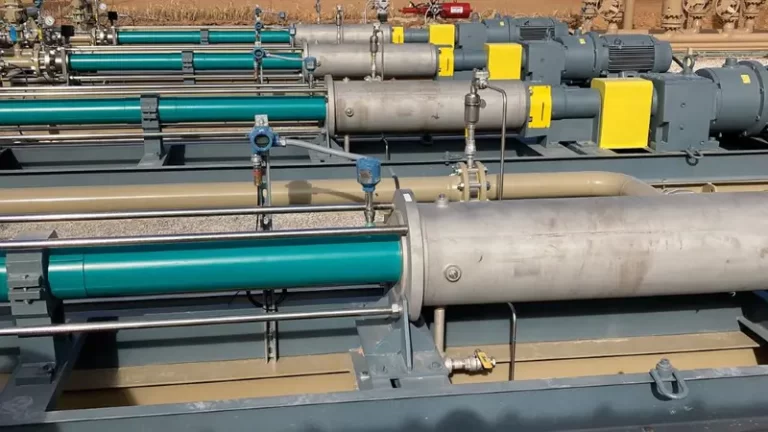
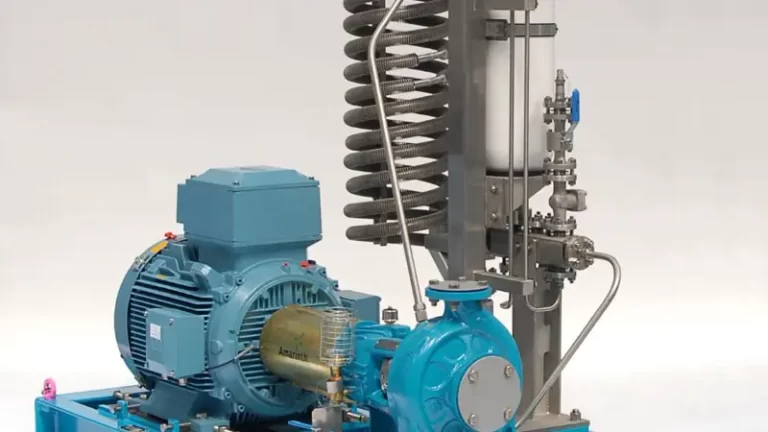
To meet the application conditions provided by the producer (7,500 bpd/51 m3/h per pump, up to 250 psi/1.7 bar suction pressures, differential pressure of 500 psi/3.4 bar) Netzsch engineers selected the Nemo pump model NM076SY. Since a total capacity of up to 30,000 bpd/204 m3/h was required from the three wells, Netzsch recommended the use of four pumps.
The Netzsch Nemo pump was supplied with SAE 316SS materials and a Nemolast S459/S91 stator.
One of the things that sets Netzsch apart from other progressing cavity pump manufacturers is the ability to offer many different universe joint options to meet demanding pumping applications. In this case, Netzsch engineers recommended the Z type joint. The Z double seal pivot joint is used when flows and pressures are high and when torque and axial loads are at their highest. This joint is oil-filled and hermetically sealed with two independent seals that are resistant and compatible to both the lubricant and the pumped fluid. It is designed for continuous, heavy duty operation under the highest loads.
The joint also has a special design with a balanced seal. The balanced seal is referred to as an equalizer. The equalizer is a sliding piston that sits in the tube coupling rod and applies pressure on the lubrication oil at the same rate the seal is pressurized from the outside. This balanced seal design is able the handle suction pressures up to 1,000 psi/69 bar.
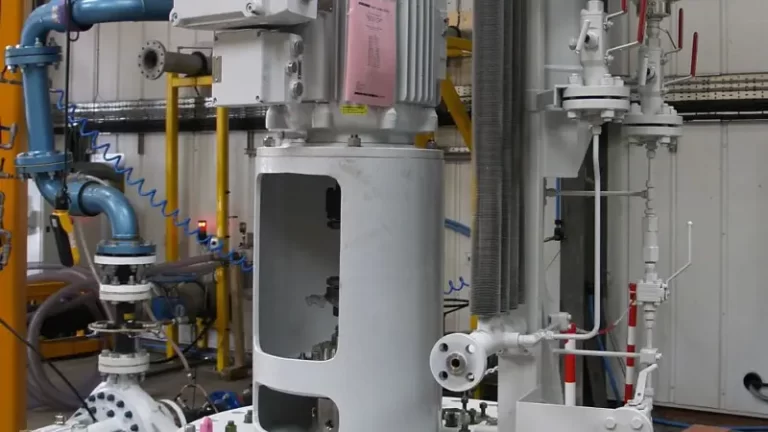
Netzsch, in partnership with DXP, supplied a complete, heavy duty I-beam skid, consisting of the pump, motor, gearbox, pressure gauges and sensors, and valves. All four pumps were installed and anchored in for smooth operation.
Engineers from DXP and Netzsch were present to ensure a smooth start-up and they have been in daily operation since.
Netzsch says that the producer has been very satisfied with the performance of the Netzsch pumps and the service and support of the Netzsch/DXP partnership. More units have been purchased and Netzsch pumps are being planned on future well sites to transport the produced water/oil mixture to central processing facilities.



 –
–





